Invictus Tariff and Trade War Recession Scenario
The Invictus Tariff and Trade War Recession 2.0 scenario (updated August 19, 2025) is intended to reflect (but not predict) a tail-risk outcome for the U.S. economy, driven by...

Author: Avik Ray , Director, Liquidity Risk Analytics
Drought conditions in Mississippi have become a growing concern, affecting various aspects of the state's economy and environment. The region has experienced a shift in precipitation patterns, leading to extended periods of water scarcity and dry spells. Rising temperatures and decreasing soil moisture exacerbate the severity and frequency of droughts in Mississippi.
These recurring drought events have far-reaching consequences for Mississippi's communities and industries. The agricultural sector, a vital component of the state's economy, heavily relies on adequate water resources for successful crop production. Droughts can diminish crop yields, increase irrigation costs, and strain farmers' livelihoods. Moreover, industries dependent on water, such as manufacturing and energy generation, face operational challenges during drought periods, impacting production capacity and economic growth.
The environmental implications of droughts are equally concerning. Reduced water levels in rivers and reservoirs threaten aquatic ecosystems, affecting fish populations, water quality, and overall biodiversity. Additionally, drought conditions contribute to an increased risk of wildfires, further endangering communities and natural habitats.
Drought risks pose significant challenges for Mississippi's communities and industries, making it imperative for community banks to play an active role in climate-related risk management. By being aware of the physical risks and their implications for loan portfolios, banks can better allocate resources, adjust lending practices, and support their customers during challenging times.
Regulators recognize the urgency of addressing climate-related risks, including drought, and have emphasized the need for banks to develop robust risk management practices. The PoWER™ analytics tool offered by Invictus Group equips community banks with the necessary insights and data to assess their exposure to drought risks accurately. By leveraging this tool, banks can visualize the specific geographic markets vulnerable to drought events and make informed decisions regarding risk mitigation and lending strategies.
To illustrate how banks can evaluate the climate related risks in their lending footprint, we can evaluate a hypothetical bank with the majority of its lending operations in the Mississippi area.
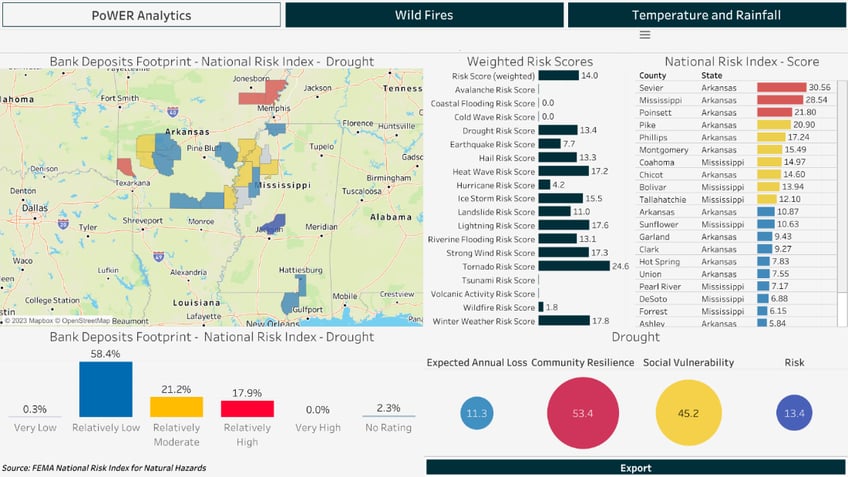
This bank has lending throughout the region, where different types of climate related risks are prevalent. We have focused on assessing the areas that have higher susceptibility to drought risk, which we can see as the areas in red on the heatmap.
Looking at the loans closest to the Mississippi river, we can see that Mississippi County in Arkansas indicates a potential area to focus on with regards to drought risk given its high Risk Score. The bank may wish to evaluate the agricultural component of the loans in this county and identify its most significant loans. By doing so, banks can work with their customers in these areas to evaluate how a drought might impact the businesses identified and work with them to ensure that plans are in place should a prolonged drought hit the region.
As the frequency and severity of droughts continue to escalate, community banks must take a proactive approach to climate risk management. By understanding the intricacies of drought risks in Mississippi and leveraging advanced analytics tools like PoWER™, banks can navigate the challenges posed by climate change, ensure financial resilience, and contribute to the sustainable development of their communities.

CECL Trends, CECL, community bank regulations, community banks, CECL Modeling, acl challenges, bank regulatory compliance, advanced cecl
Now that most community banks have eight to ten quarters of CECL experience under their belts, many are still grappling with foundational issues such as overreliance on qualitative factors, lack of responsiveness to risk rating...

capital planning, community bank regulations, Deregulation, bank strategy, community banks, regulatory capital, bank growth strategy, cre risk
Author : Adam Mustafa, CEO, Invictus Analytics
Community banks now have the clearest path in nearly two decades to reshape their regulatory capital requirements—and they shouldn't miss it. While most recent efforts to ease...